Building Your Incident Management System: Business Continuity and Incident Response Standards ISO 22301 and ISO 22320
911Cellular
|
For organizations with essential or significant operations, it is necessary to build a resilient infrastructure ready to face any disruption. The Business Continuity and Incident Response Standards ISO 22301 and ISO 22320 provide a fundamental framework for Critical Incident Management (CIM), including incident communication systems and business continuity. These internationally recognized standards guide organizations in developing, implementing and optimizing systems that effectively navigate disruptions - protecting operations and stakeholders.
Overview of ISO 22301 and ISO 22320?
ISO 22301 and ISO 22320 are internationally recognized management standards that provide a structured approach to business continuity and incident response, helping organizations manage disruptions effectively. ISO 22301 is a comprehensive business continuity management system, while ISO 22320 is a CIM standard. Both frameworks enhance organizational resilience, preparing teams to respond quickly and efficiently to any incident.
Key Benefits of ISO 22301 and ISO 22320
- Enhanced Resilience, Preparedness and Resource Efficiency: ISO 22301 and ISO 22320 provide a structured approach to risk assessment, continuity planning and incident response coordination, helping organizations identify critical business functions and streamline communication and command structures. With this framework, organizations are better prepared for disruptions, ensuring effective resource allocation for sustained operations and seamless coordination across teams and agencies. This minimizes delays and miscommunication during critical situations.
- Reduced Downtime and Operational Impact from Incidents: Proactively identifying potential threats and having a structured response plan allows organizations to minimize downtime and maintain operations during a critical incident, reducing financial and operational losses while preserving essential services.
- Regulatory Compliance and Reputation Management: Compliance with ISO standards is recognized worldwide and demonstrates a commitment to best practices in crisis management and business continuity. This commitment can enhance trust with clients, regulatory bodies, and other stakeholders, strengthening the organization’s reputation as a responsible, prepared entity.
ISO 22301: Business Continuity Management Systems
This structure simplifies the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) into core business processes, enhancing efficiency and promoting senior management involvement. The standard operates on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, which drives continuous improvement across all processes and the BCMS. The system is highly adaptable and scalable, meaning each business will have different needs and elements included in the plan.
Key elements include:
- Organization: The internal and external factors impacting business continuity.
- Interested Parties: Stakeholders (e.g., suppliers, customers) who may influence or be influenced by BCMS decisions.
- Leadership: Requirements for top management’s role in directing the BCMS.
- Performance Evaluation: Methods to measure and evaluate BCMS effectiveness.
- Maximum Acceptable Outage (MAO): The longest acceptable disruption time.
- Minimum Business Continuity Objective (MBCO): The minimal level of services/products required during a disruption.
- Prioritized Timeframes: Recovery order and timing for essential activities.
- Warning and Communication: Incident-related actions to ensure coordinated response.
These elements, structured around PDCA, help organizations ensure effective and resilient continuity management.
ISO 22320: Incident Management
ISO 22320 promotes a systematic, objective-based approach to incident response, closely aligned with the National Incident Management System (NIMS). It emphasizes the involvement of all personnel in the process, including observation, data gathering, assessment, and decision-making.
Incident Management Structure
The ISO 22320 operating structure includes five core functions: Command, Planning, Operations, Logistics, and Finance and Administration, each tailored to ensure a coordinated response.
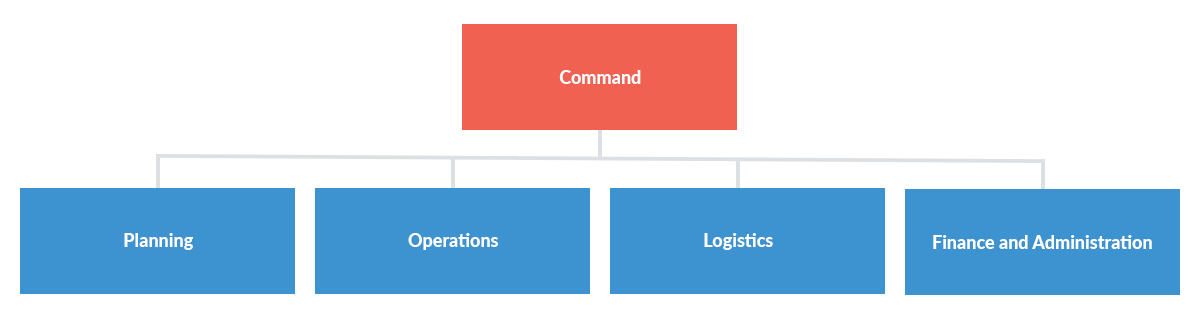
- Command: Holds authority over the incident, overseeing incident objectives, assigning responsibilities and managing resource orders.
- Planning: Responsible for collecting, evaluating and sharing incident information and documenting and updating the incident action plan to align with evolving conditions.
- Operations: Addresses tactical objectives, focusing on hazard reduction, protecting people and property and guiding the incident through the response phase into recovery.
- Logistics: Manages resources and support, coordinating facilities, transportation, supplies, and communication support essential for personnel involved in the response.
- Finance and Administration: Addresses compensation, procurement and time management. Smaller incidents may not always require a separate function for financial oversight.
This structure allows organizations to maintain a consistent, hierarchical incident response across different levels, with the flexibility to scale up or down as necessary.
Incident Management Process
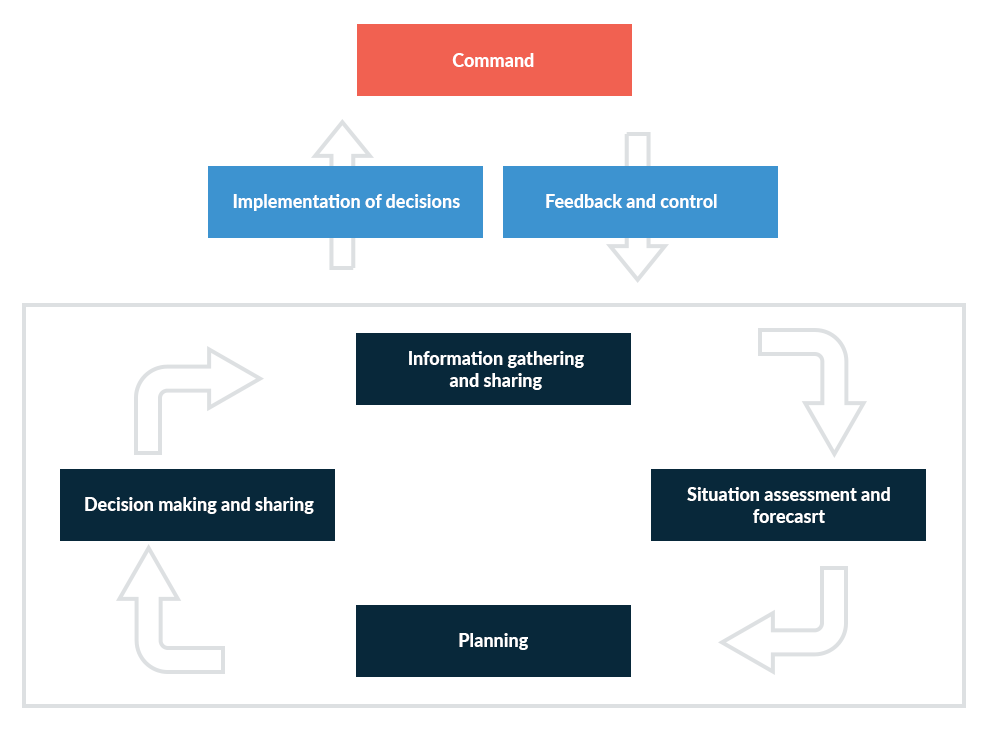
ISO 22320 is an incident management system that covers proactive planning and emergency response. Organizations will create an Incident Action Plan (IAP) during the planning process that defines goals, tactics and resource management. Though IAPs help align resources and response team efforts, which cut down on response times and incident durations, ISO also acknowledges the importance of agile responses during an incident. ISO 22320’s management process emphasizes a continuous, team-wide approach to observation, assessment, planning and decision-making, encouraging organizations to anticipate cascading effects, manage timelines and respond proactively to evolving needs. This approach applies to short- and long-term incidents and supports a comprehensive, scalable response structure adaptable to different levels of responsibility within the organization.
Integrating ISO 22301 and ISO 22320 into Your Other Management Systems
ISO 22301 follows the Annex SL high-level structure, a common framework for all new management system standards. This ensures consistency across various standards, aligns sub-clauses, and employs unified language. The structure simplifies the integration of the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) into core business processes, which enhances efficiency and promotes involvement from senior management.
ISO 22320 can complement ISO 22301 by providing additional emergency management and response protocols; However, integrating ISO 22320 into other systems may require more customization since it is a guidance standard and not an Annex SL management system. Incorporating ISO 22320 into the broader business continuity framework of ISO 22301 allows organizations to leverage both standards for a more comprehensive CIM strategy.
Building a Resilient Future
Incorporating ISO 22301 and ISO 22320 standards is a decisive step toward building a resilient and prepared organization. By aligning with these best practices, leaders can establish an adaptable CIM framework that protects their organization’s people, processes, and reputation. Embracing this proactive approach to business continuity and incident response is essential in today’s volatile environment, positioning your organization to thrive—even in the face of uncertainty.
Learn even more about critical incident managament at 911Cellular.com.
Related Articles
Alyssa’s Act of 2025: A Renewed Push for Federal School Safety Standards
Alyssa’s Act of 2025: A Renewed Push for Federal School Safety Standards Alyssa’s Act has returned...
Preparing for a Safe Semester: Why Now is the Perfect Time to Test Your Emergency Notification System
With students back on campus and routines settling in after winter break, colleges and universities...
UTC launches new campus safety system from 911Cellular
The University of Tennessee at Chattanooga has announced a partnership with 911Cellular to deploy a...
The Healthcare Staffing Crisis is a Safety Crisis
Hospitals everywhere are confronting a hard truth: the global nurse staffing shortage isn’t just...
Why Nurses Are Reaching Their Limit– and What Hospitals Can Improve Right Now
The nursing shortage is no longer breaking news. Hospital leaders know the workforce is strained,...
The Social Side of Under-Reporting in Healthcare
Under-reporting workplace violence in healthcare isn’t driven by one issue– it’s built from layers.